In today’s fast world, the dividing line that separated work from personal life is increasingly being blurred. Anxiety and stress have grown as major determinants for mental health due to the increasing demands of present-day work environments. Whether it be stress for meeting deadlines, expected output efficiency, or striking a balance between work and life, these stressors are taking their toll on employees’ overall well-being. Understanding how anxiety and work stress impinge on workers and the workplace will be important in developing healthier work environments and ensuring long-term productivity and mental health.
The Prevalence of Anxiety and Work Stress in the US
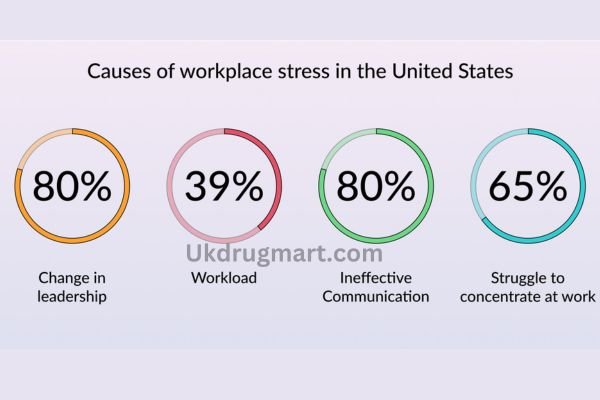
The American Psychological Association presents work-related stress as an epidemic in the United States. In 2022, a survey showed that about 60% of American adults reported feeling stressed at work, with a large portion of the population experiencing chronic anxiety related to their job responsibilities. Anxiety disorders afflict about 19% of adults in the US, and these are often triggered or worsened by work pressures that manifest in a variety of physical and emotional symptoms.
Anxiety in the workplace isn’t confined to those high-stress professions. Employees from technology and finance to education and healthcare can be afflicted. Indeed, studies have found that jobs requiring continuous multitasking, long hours, or tight deadlines are among the most common culprits in work-related anxiety. The “always-on” culture, which requires workers to be accessible at any time, has also contributed to increased levels of stress and anxiety.
Anxiety and Stress Symptoms in the Workplace

Anxiety and work stress manifest both physically and emotionally in different ways. Some of the signs to look out for in employees who are suffering from high levels of anxiety include:
Physical symptoms:
Frequent headaches, digestive problems, muscle tension, and fatigue.
Emotional symptoms:
Feeling overwhelmed, excessive worry about job performance, or experiencing feelings of dread before going to work.
The psychological manifestations are:
Behavioral symptoms-
food avoidance, procrastination, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and inability to unwind during breaks or after work hours.
Sleep disturbances
The failure of proper or complete sleep due to overwhelming cognitions from work.
These symptoms not only affect the individual’s quality of life but also impact productivity and performance at work. In extreme conditions, anxiety and stress may lead to burnout—a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged stress.
Work Stress and Anxiety: The Impact on Employee Health

Chronic work stress and anxiety are associated with a wide range of health problems. Long-term stress can raise the vulnerability to serious conditions such as the following:
Cardiovascular disease:
Long-term stress is also known to increase blood pressure, hence increasing heart disease and stroke.
Mental health disorders:
Anxiety is capable of bringing on depression, panic disorders, and other mental disorders.
Compromised immune system:
The result of stress weakening the body’s immune reaction against infections can be observed in increased sick days and absenteeism.
Substance abuse:
People experiencing a high degree of work-related stress can engage in substance abuse as an ineffective coping mechanism for their anxiety.
Musculoskeletal disorders:
Muscle tension due to stress can result in chronic conditions such as back pain and headaches.
Besides the individual health effects, these problems tend to lead to increased health care costs for employers and a general decrease in overall productivity within the workplace.
Work-Related Stress and Anxiety Across Occupations
Although anxiety and stress can affect all industries and sectors, there are particular ones where high levels of work-related stress are recorded. Among these are:
Healthcare:
Physicians, nurses, and other emergency responders have to work for long periods under high pressure. The emotional demands of patient care and life-and-death decision-making can easily result in burnout and anxiety of the worst kind. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Nursing, healthcare workers experience some of the highest levels of job-related stress.
Technology:
The tech industry is notorious for demanding long hours and tight deadlines. In addition, the constant need for innovation, along with the fast pace of the field, can lead to burnout and stress in employees. Tech workers also feel isolated, especially with the rise of remote work, which can exacerbate anxiety.
Finance:
Financial services are usually a high-stakes affair, with professionals under the compulsion of meeting performance targets, handling large sums of money, and operating through volatile markets. The unending stress, apart from long working hours, is the main cause of both physical and mental health problems.
Education:
Teachers and educators face the stress of managing large classrooms, meeting academic standards, and supporting students’ diverse needs. Added pressure from parents and administration, combined with low pay in some areas, can increase anxiety and lead to high turnover rates.
Customer Service and Retail:
Customer service or retail employees often have to put up with rude customers, long shifts, and irregular working hours. Pressures to meet sales targets and maintaining a good attitude can result in very stressful and anxious situations.
Coping with Anxiety and Stress at Work
Both employers and employees should be aware of the signs of anxiety and stress and take active measures to combat them. The following are some ways of coping with work-related stress and anxiety:
1. Workplace Mental Health Programs
Employers should prioritize mental health by providing programs and resources that support employees dealing with anxiety and stress. This can include Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs), counseling services, and workshops on stress management. Creating a safe, open environment where employees feel comfortable discussing mental health is crucial.
2. Flexible Work Hours and Remote Work Options
Offering flexible work hours and the ability to work remotely can help alleviate stress. This allows employees to balance their work and personal lives more effectively, reducing the anxiety associated with commuting and tight schedules.
3. Encourage Breaks and Time Off
Taking regular breaks during the day, as well as vacation days, can help employees recharge and reduce stress. Encouraging employees to take time off to focus on their mental health without fear of judgment or consequences is essential for reducing work-related anxiety.
4. Promote a Healthy Work-Life Balance
Employers should have a balance between work and life to enable employees to draw a line between these two. This may mean discouraging the practice of answering emails or taking calls after work hours to create a culture that values time with the family or friends.
5. Mindfulness and Stress-Reduction Techniques
Mindfulness practices, meditation, and stress-reduction exercises allow employees to manage anxiety on the spot. Workshops or resources on these techniques may give employees the necessary tools to quiet their minds and keep them focused.
6. Allow Mental Health Days
Allowing employees to take off days for mental health when they are overwhelmed prevents burnout and enables them to return to work refreshed. These days should be treated as a necessity for the overall well-being of the employee, rather than a luxury.
Conclusion
Anxiety and work stress are increasing concerns among American workers, affecting employees in almost every industry. The effects of stress on poor mental health, physical ill health, and loss of productivity can be very destructive, not only for the individuals but also for their employers. But by comprehending the origins of job-related anxiety and the measures aimed at reducing it, an employer can create an environment healthier and more supportive of employee well-being and efficiency. For employees, seeking help when needed and developing healthy coping mechanisms are very important for managing anxiety and maintaining a balanced, fulfilling career. The focus on mental health in the workplace is more important than ever in creating a workforce that is not only productive but also healthy and thriving.

Leave a Reply