Sleep is an essential part of life, yet many people experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep at some point. While occasional sleep disturbances are common, chronic insomnia and temporary sleep issues are two distinct conditions that can significantly impact your well-being. Understanding the differences between these two types of sleep problems is crucial for identifying the right approach to treatment and improving overall health.
In this blog post, we will explore what chronic insomnia is, how it differs from temporary sleep issues. And the causes behind each, and the best ways to manage them.
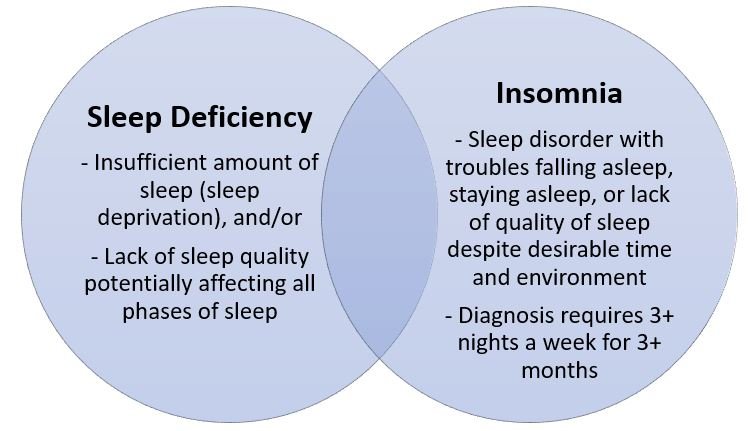
What is chronic Insomnia?

Chronic insomnia is a long-term sleep disorder that affects individuals for at least three times a week. Lasting for at least three months or more. People with chronic insomnia experience persistent difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep. Or waking up too early and not being able to return to sleep. This condition can significantly disrupt daily functioning, leading to fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and decreased overall quality of life.
Chronic insomnia can occur on its own (primary insomnia) or as a result of other underlying health conditions (secondary insomnia). The causes of chronic insomnia are often complex, involving a combination of psychological, behavioral, and physiological factors. Anxiety, depression, stress, certain medications, and medical conditions like chronic pain or sleep apnea can contribute to chronic insomnia.
What are Temporary Sleep Issues?
Temporary sleep issues, also known as short-term insomnia, are brief disruptions in sleep that last for a few days to a few weeks. These disturbances are often triggered by specific factors, such as stress, travel, jet lag, a change in routine, or the consumption of caffeine or alcohol before bedtime. Unlike chronic insomnia, temporary sleep problems typically resolve on their own once the underlying cause is addressed or removed.
While temporary sleep issues can affect anyone, they are usually short-lived and do not lead to long-term health problems. Many individuals experience temporary insomnia at some point in their lives due to factors like work deadlines, emotional stress, or a hectic lifestyle. Once the stressor is removed or resolved, sleep typically returns to normal without the need for medical intervention.
Key Differences Between Chronic Insomnia and Temporary Sleep Issues

- Duration
- Causes
- Chronic Insomnia: Chronic insomnia may be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Psychological Factors: Anxiety, depression, or stress can significantly impact sleep patterns.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like chronic pain, asthma, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome can interfere with sleep.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as stimulants, antidepressants, or blood pressure medications, may contribute to insomnia.
- Behavioral Factors: Poor sleep hygiene, excessive screen time before bed, or an irregular sleep schedule can exacerbate chronic insomnia.
- Temporary Sleep Issues: Temporary sleep disturbances are typically triggered by external factors, such as:
- Stress: Work deadlines, family issues, or major life changes can cause temporary insomnia.
- Travel: Jet lag or irregular sleep patterns during travel can disrupt sleep.
- Dietary Habits: Consumption of caffeine, alcohol, or heavy meals close to bedtime can interfere with sleep.
- Chronic Insomnia: Chronic insomnia may be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Impact on Daily Life
- Chronic Insomnia: The effects of chronic insomnia are long-lasting and can severely impact a person’s quality of life. Individuals may experience fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and a decreased ability to perform daily tasks. Chronic insomnia can also contribute to the development of other health conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
- Temporary Sleep Issues: While temporary sleep problems can be disruptive, they typically do not have the same long-term effects as chronic insomnia. Once the underlying cause is resolved, sleep usually returns to normal, and any daytime fatigue or irritability tends to subside.
- Treatment Approaches
- Chronic Insomnia: Treating chronic insomnia often requires a multifaceted approach. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is considered one of the most effective treatments, helping individuals identify and change thoughts and behaviors that contribute to poor sleep. In some cases, medications such as sedative-hypnotics or antidepressants may be prescribed. Lifestyle changes, such as improving sleep hygiene, relaxation techniques, and regular exercise, can also help manage chronic insomnia.
- Temporary Sleep Issues: For temporary sleep disturbances, treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause. This may include managing stress, improving sleep hygiene, avoiding stimulants, and making lifestyle changes. Short-term use of over-the-counter sleep aids may be considered, but they should not be relied upon for extended periods. Once the triggering factor is resolved, normal sleep patterns usually resume.
- Prognosis
- Chronic Insomnia: Chronic insomnia often requires ongoing management and lifestyle adjustments to prevent relapse. It is important for individuals with chronic insomnia to seek professional help to address the underlying causes and improve their sleep.
- Temporary Sleep Issues: The prognosis for temporary sleep issues is generally favorable. Once the trigger is identified and resolved, most individuals can return to their normal sleep routine without long-term consequences.
How to Manage Sleep Issues
Whether you are dealing with chronic insomnia or temporary sleep disturbances, there are several strategies that can help improve your sleep quality:
- Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Create a consistent bedtime routine, keep your sleep environment cool and dark, and avoid stimulating activities before bed, such as watching TV or using electronic devices.
- Manage Stress: Stress is one of the most common triggers of both chronic insomnia and temporary sleep issues. Engage in relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, to reduce stress levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can promote better sleep. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep, so it’s best to avoid them several hours before bedtime.
- Seek Professional Help: If your sleep issues persist, it’s important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can help identify the underlying cause of your sleep problems and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion
In summary, chronic insomnia and temporary sleep issues are two distinct conditions with different causes, durations, and impacts on daily life. While temporary sleep problems are usually short-lived and resolve on their own, chronic insomnia can have long-term effects on physical and mental health. Understanding the differences between these two types of sleep disturbances can help you identify the appropriate course of action to improve your sleep and overall well-being.
By prioritizing good sleep hygiene, managing stress, and seeking professional help when necessary, you can enhance your sleep quality and lead a healthier, more productive life.

Leave a Reply