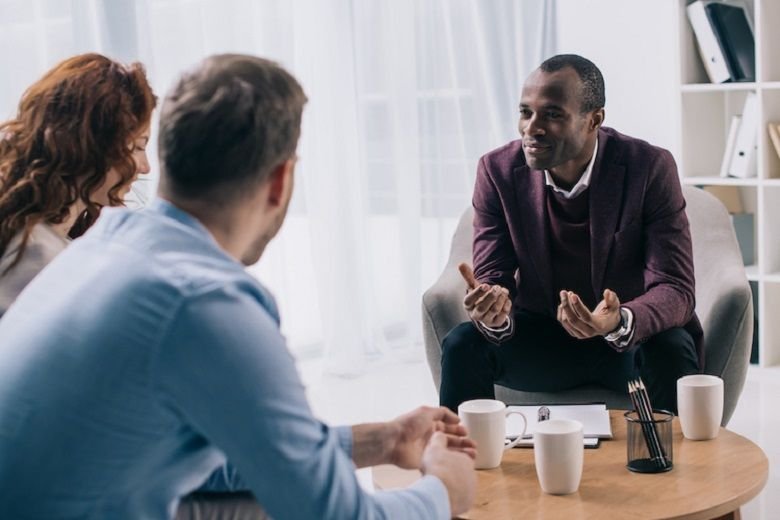

Chronic anxiety disorders affect millions of individuals worldwide, making it one of the most prevalent mental health conditions today. While many people experience occasional anxiety, chronic anxiety is a persistent and overwhelming form of stress that can significantly interfere with daily life. Therapy has emerged as one of the most effective ways to manage and treat chronic anxiety disorders. By understanding the role of therapy, individuals can take an important step toward reclaiming their mental health and well-being.
Understanding Chronic Anxiety Disorders

Before delving into the role of therapy, it is essential to understand what constitutes chronic anxiety disorders. These disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Symptoms often include excessive worry, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, irritability, physical tension, and sleep disturbances. Unlike situational anxiety, chronic anxiety disorders persist for months or years and require professional intervention to address underlying causes.
The Importance of Therapy
Therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for anxiety disorders. Unlike medication, which focuses on symptom relief, therapy aims to address the root causes of anxiety and equip individuals with tools to cope effectively. Here are several reasons therapy plays a pivotal role in managing chronic anxiety:
- Identifying Underlying Causes:Therapy helps uncover the underlying factors contributing to anxiety. These may include unresolved trauma, negative thought patterns, or environmental stressors. By identifying these triggers, therapists can create a personalized treatment plan.
- Developing Coping Strategies: Therapy equips individuals with practical coping mechanisms to manage anxiety in real-time. These strategies can include breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, and problem-solving techniques.
- Addressing Negative Thought Patterns: Many chronic anxiety disorders are fueled by distorted thinking patterns, such as catastrophizing or black-and-white thinking. Therapy helps individuals recognize and reframe these thoughts, leading to a more balanced perspective.
- Building Emotional Resilience: Over time, therapy fosters emotional resilience, empowering individuals to handle stress and uncertainty more effectively. This resilience is essential for long-term management of anxiety.
Types of Therapy for Chronic Anxiety Disorders

Several therapeutic approaches have proven effective in managing chronic anxiety. Each method offers unique tools and perspectives tailored to different needs:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is one of the most widely used and evidence-based therapies for anxiety. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Key techniques in CBT include:
- Cognitive Restructuring: Replacing irrational thoughts with more realistic and positive ones.
- Exposure Therapy: Gradually confronting feared situations or stimuli in a controlled environment to reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Behavioral Experiments: Testing the validity of anxious thoughts through real-life experiments.
CBT is highly effective for disorders like GAD, social anxiety, and panic disorder, offering both immediate and long-term benefits.
2. Mindfulness-Based Therapies
Mindfulness-based approaches, such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) and Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), emphasize staying present and accepting thoughts without judgment. These therapies teach individuals to observe their anxiety without reacting to it, which can reduce its intensity over time.
3. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Originally developed for borderline personality disorder, DBT has been adapted for anxiety management. It focuses on emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. DBT is particularly helpful for individuals with severe anxiety accompanied by emotional dysregulation.
4. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
ACT encourages individuals to accept their anxiety rather than fight it, while committing to actions aligned with their values. This approach helps individuals focus on living a meaningful life, even in the presence of anxiety.
5. Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy explores unconscious processes and past experiences that may contribute to chronic anxiety. By gaining insight into these hidden factors, individuals can address unresolved issues and achieve emotional healing.
6. Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP is particularly effective for OCD. It involves exposing individuals to anxiety-provoking situations or thoughts without engaging in compulsive behaviors. Over time, this reduces the association between the trigger and the anxiety response.
The Therapeutic Process
The therapeutic process begins with an initial assessment, during which the therapist gathers information about the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and personal goals. Based on this assessment, a customized treatment plan is developed. Sessions typically involve:
- Establishing Trust: Building a strong therapeutic relationship is essential for effective treatment.
- Goal Setting: Collaborating on achievable and measurable goals for managing anxiety.
- Skill Building: Learning practical tools and techniques to reduce anxiety.
- Ongoing Evaluation: Regularly assessing progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
Combining Therapy with Other Treatments
While therapy is highly effective on its own, it is often combined with other treatments for comprehensive care. For example:
- Medication: Anti-anxiety medications or antidepressants may be prescribed alongside therapy to help manage severe symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep complement the therapeutic process.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide additional support and reduce feelings of isolation.
The Benefits of Therapy

Therapy offers numerous benefits beyond anxiety management. It improves overall emotional well-being, enhances self-awareness, and fosters healthier relationships. For individuals with chronic anxiety, therapy provides a safe space to explore their feelings, gain insights, and develop lasting strategies for coping.
Overcoming Barriers to Therapy
Despite its benefits, many individuals hesitate to seek therapy due to stigma, financial constraints, or uncertainty about what to expect. Overcoming these barriers is essential for accessing the help needed to manage chronic anxiety. Online therapy options, sliding-scale fees, and community mental health programs can make therapy more accessible.
Conclusion
Therapy plays a vital role in managing chronic anxiety disorders by addressing the root causes of anxiety, equipping individuals with effective coping strategies, and fostering long-term emotional resilience. With various therapeutic approaches available, individuals can find a method that suits their unique needs and preferences. By seeking therapy, those with chronic anxiety can take a crucial step toward a calmer, more fulfilling life. Overcoming anxiety is a journey, but with the right tools and support, it is entirely achievable.

Leave a Reply